H-ARC: A Comprehensive Behavioral Dataset for the Abstraction and Reasoning Corpus
Solim LeGris, Wai Keen Vong, Brenden M. Lake and Todd M. Gureckis
New York University
How well do people reason about abstract visual program synthesis problems?
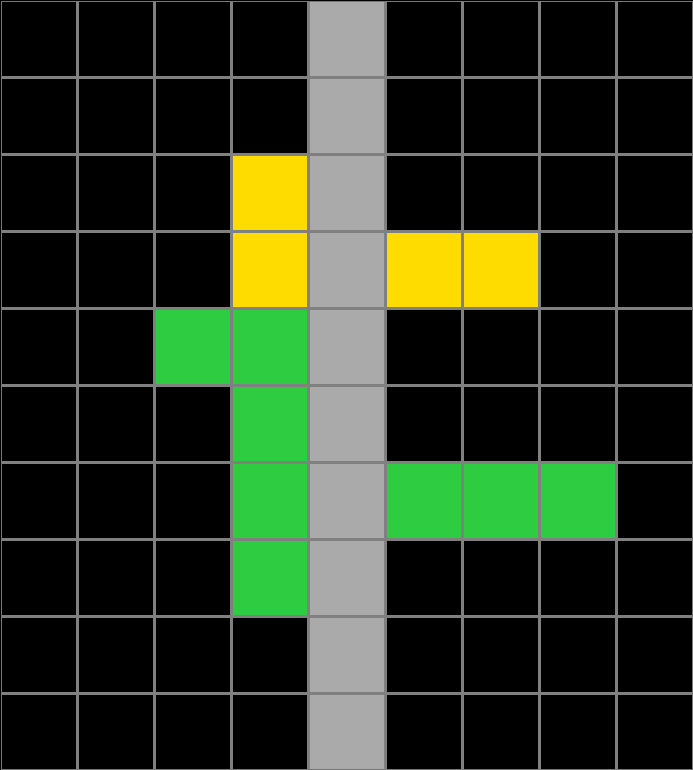
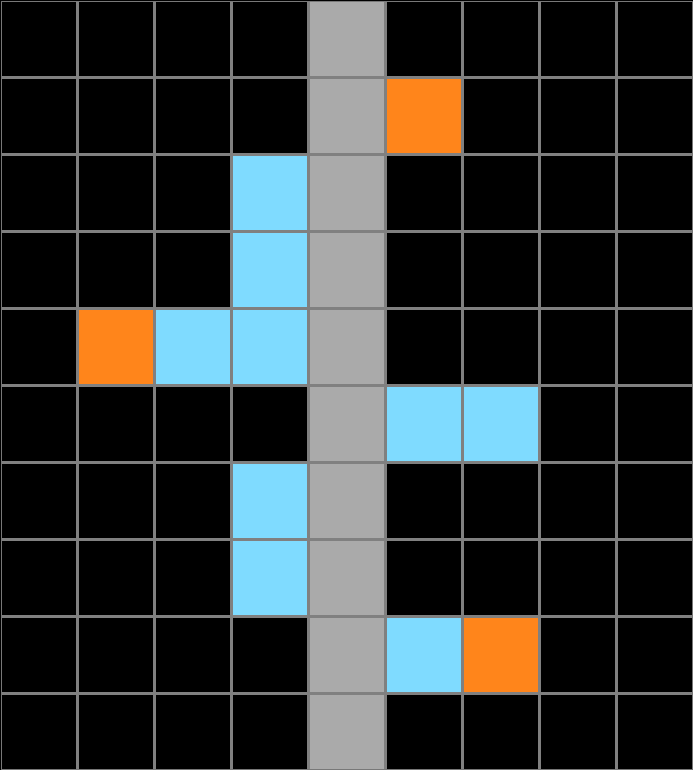
Training examples
People were asked to infer an underlying rule or program using training examples from 5 randomly select problems.
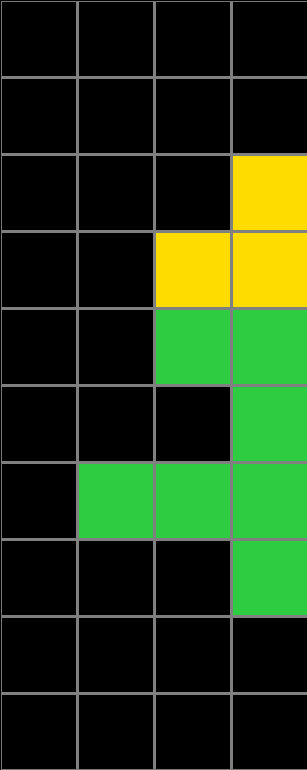
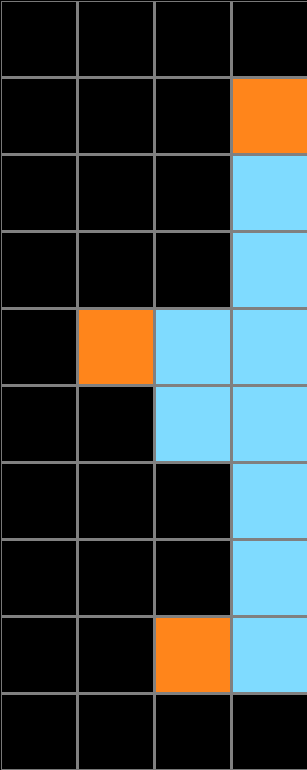
Test Example
Using their inferred rule or program, people were asked to generate an output for a given test input in three attempts or less.
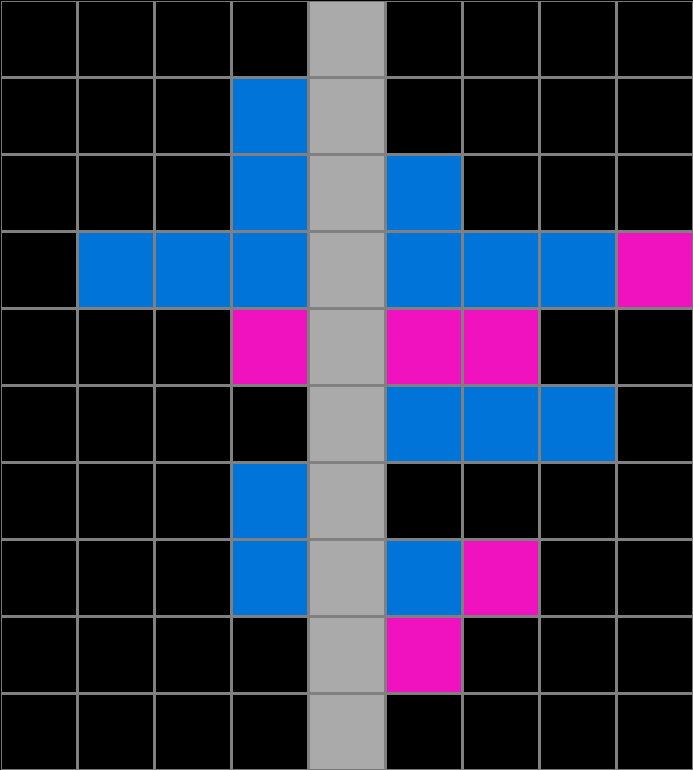
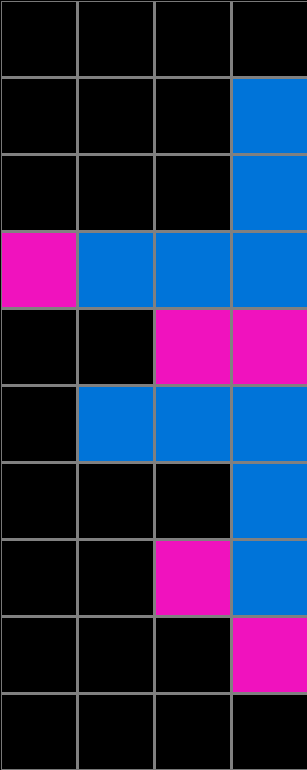
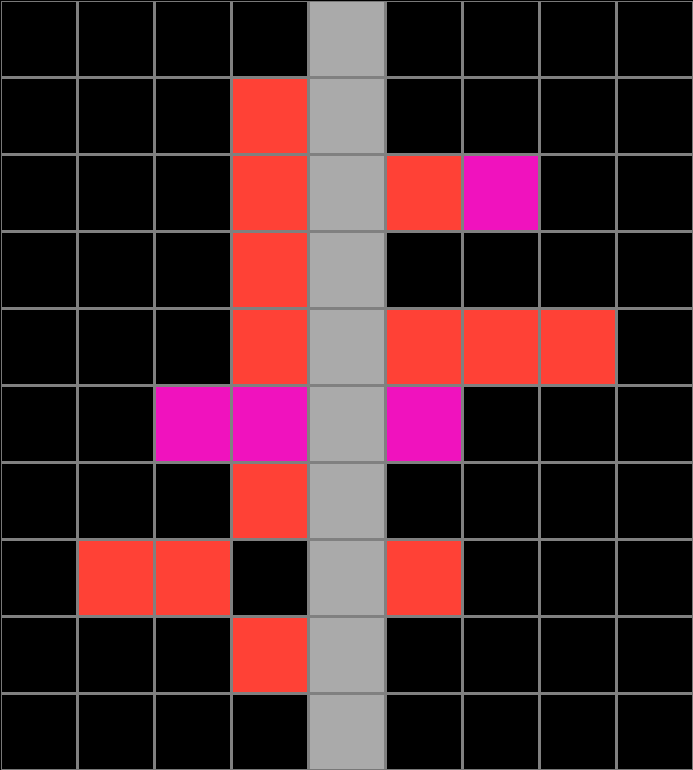
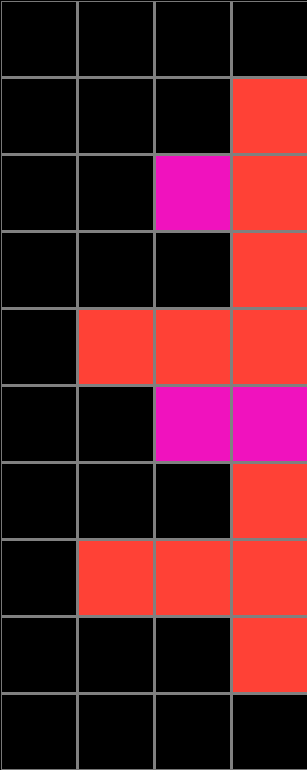
State Space Graph
We collected action by action data from 1729 participants. The graph below shows visited states from all participants that attempted the particular task shown here.
Explore H-ARC
Explore participant responses, natural language descriptions, errors and state space graphs for tasks from the training and evaluation sets.
Abstract
The Abstraction and Reasoning Corpus (ARC) is a visual program synthesis benchmark designed to test out-of-distribution generalization in machines. Comparing AI algorithms to human performance is essential to measure progress on these problems. In this paper, we present H-ARC (Human-ARC): a novel large-scale dataset containing solution attempts from over 1700 humans on ARC problems. The dataset spans the full set of 400 training and 400 evaluation tasks from the original ARC benchmark, and it is the largest human evaluation to date. By publishing the dataset, we contribute human responses to each problem, step-by-step behavioral action traces from the ARC user-interface, and natural-language solution descriptions of the inferred program/rule. We believe this dataset will be of value to researchers, both in cognitive science and AI, since it offers the potential to facilitate the discovery of underlying mechanisms supporting abstraction and reasoning in people. The insights to be gained from these data not only have value for cognitive science, but could in turn inform the design of more efficient, human-like AI algorithms.